Addressable RGB LED Control#
Harness the power of addressable RGB LED strips with the PULSAR H2 board. Learn how to control intelligent RGB LED strips and create dazzling lighting effects using MicroPython.
This section describes how to control addressable RGB LED strips (WS2812/WS2811 compatible) using the PULSAR H2 board. The PULSAR H2 board has a GPIO pin embedded connected to a single addressable RGB LED.
PIN |
GPIO ESP32H2 |
|---|---|
DIN |
8 |
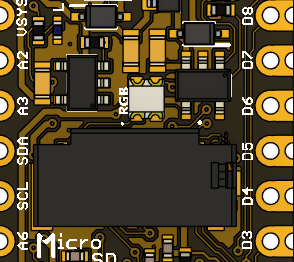
Fig. 24 Addressable RGB LED Strip#
Code Example#
Below is an example that demonstrates how to control addressable RGB LED strips using the PULSAR H2 board
from machine import Pin
from neopixel import NeoPixel
# Initialize addressable RGB LED on GPIO8
rgb_led = NeoPixel(Pin(8), 1)
# Set color (Red, Green, Blue) - orange color
rgb_led[0] = (255, 128, 0)
# Apply the color change
rgb_led.write()
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define RGB_LED_PIN 8
#define NUM_LEDS 1
// Initialize addressable RGB LED strip
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS, RGB_LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
strip.begin();
// Set color (Red, Green, Blue) - orange color
strip.setPixelColor(0, 255, 128, 0);
strip.show();
}
void loop(){}
#include <stdio.h>
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "driver/rmt_tx.h"
#include "esp_err.h"
void app_main(void) {
rmt_channel_handle_t tx_channel = NULL;
rmt_tx_channel_config_t tx_config = {
.gpio_num = GPIO_NUM_8,
.clk_src = RMT_CLK_SRC_DEFAULT,
.resolution_hz = 10000000, // 10MHz resolution, 1 tick = 0.1us
.mem_block_symbols = 64,
.trans_queue_depth = 4,
.flags.invert_out = false,
.flags.with_dma = false,
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_new_tx_channel(&tx_config, &tx_channel));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_enable(tx_channel));
rmt_encoder_handle_t bytes_encoder = NULL;
rmt_bytes_encoder_config_t bytes_encoder_config = {
.bit0 = {.level0 = 1, .duration0 = 3, .level1 = 0, .duration1 = 9}, // 0: ~0.3us high, ~0.9us low
.bit1 = {.level0 = 1, .duration0 = 9, .level1 = 0, .duration1 = 3}, // 1: ~0.9us high, ~0.3us low
.flags.msb_first = true,
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_new_bytes_encoder(&bytes_encoder_config, &bytes_encoder));
rmt_transmit_config_t tx_trans_config = {
.loop_count = 0,
};
uint8_t r = 255, g = 0, b = 0;
while (1) {
if (r == 255 && g < 255 && b == 0) {
g++;
} else if (g == 255 && r > 0 && b == 0) {
r--;
} else if (g == 255 && b < 255 && r == 0) {
b++;
} else if (b == 255 && g > 0 && r == 0) {
g--;
} else if (b == 255 && r < 255 && g == 0) {
r++;
} else if (r == 255 && b > 0 && g == 0) {
b--;
}
uint8_t color_data[3] = {g, r, b};
// printf("%d %d %d\n",r,g,b);
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_transmit(tx_channel, bytes_encoder, color_data, sizeof(color_data), &tx_trans_config));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_tx_wait_all_done(tx_channel, portMAX_DELAY));
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(10));
}
}
Tip
Compatibility Note: This addressable RGB LED is compatible with WS2812/WS2811 protocols. For more information on the MicroPython implementation, refer to the NeoPixel Library Documentation.
Supported Protocols: WS2812, WS2812B, WS2811, SK6812 and other compatible addressable RGB LEDs.
